Introduction
If you have run much publicly available GAUSS code, you have probably come across the #include command. Since it is used so much, it will be helpful to answer these questions:
- What does
#includedo? - What is the most common error when using
#include? - How can I resolve the most common error?
What does #include do?
The #include command is almost exactly like an instruction telling GAUSS to copy-and-paste the contents of one file into another. It is often used so that a file containing procedures and/or control variables can be kept separate from the main code file.
Example without #include
For example, let's imagine we have a file named hypotenuse.gss with the following contents:
a = 3; b = 4; c = hypotenuse(a, b); proc (1) = hypotenuse(a,b); retp(sqrt(a.^2 + b.^2)); endp;
We can run this file and it will assign c to be equal to 5 as we expect.
Example with #include
If we will only ever want to use the hypotenuse procedure in this one file, then it is probably fine to leave it as it is. However, if this procedure will be reused a lot, it might be better to just have one copy of the procedure, instead of copy-and-pasting the procedure every time we need to use it.
To do this, we would break our hypotenuse.gss file up into two files, main.gss and hypotenuse.src. The contents of main.gss will be:
a = 3; b = 4; c = hypotenuse(a,b); // Make hypotenuse procedure available #include hypotenuse.src
and the contents of hypotenuse.src will be:
proc (1) = hypotenuse(a,b); retp(sqrt(a.^2 + b.^2)); endp;
As long as GAUSS can find the hypotenuse.src file, these versions will behave identically.
The most common #include error
By far the most common error occurs when GAUSS cannot find the #include'd file. If GAUSS could not find our hypotenuse.src file, we would get an error like this:
G0014 : File not found 'C:\gauss\examples\hypotenuse.src'
Where does GAUSS look for the #include file?
When shown an error message stating that the file cannot be found in a directory such as C:\gauss\examples\, people often wonder why GAUSS looked for the file in their GAUSS examples directory. GAUSS did search in the directory found in the error message. However, that is the last place that GAUSS looked.
The GAUSS #include command will search the following locations, in this order:
- Your current working directory.
- The files in your SRC_PATH.
How can I resolve the problem?
If GAUSS cannot find a #include'd file you can fix the problem by either:
- Changing your GAUSS working directory to the folder in which the file is located.
- Moving the file to one of the GAUSS SRC_PATH locations.
- Adding a full path to the
#includestatement.
The second most common #include error
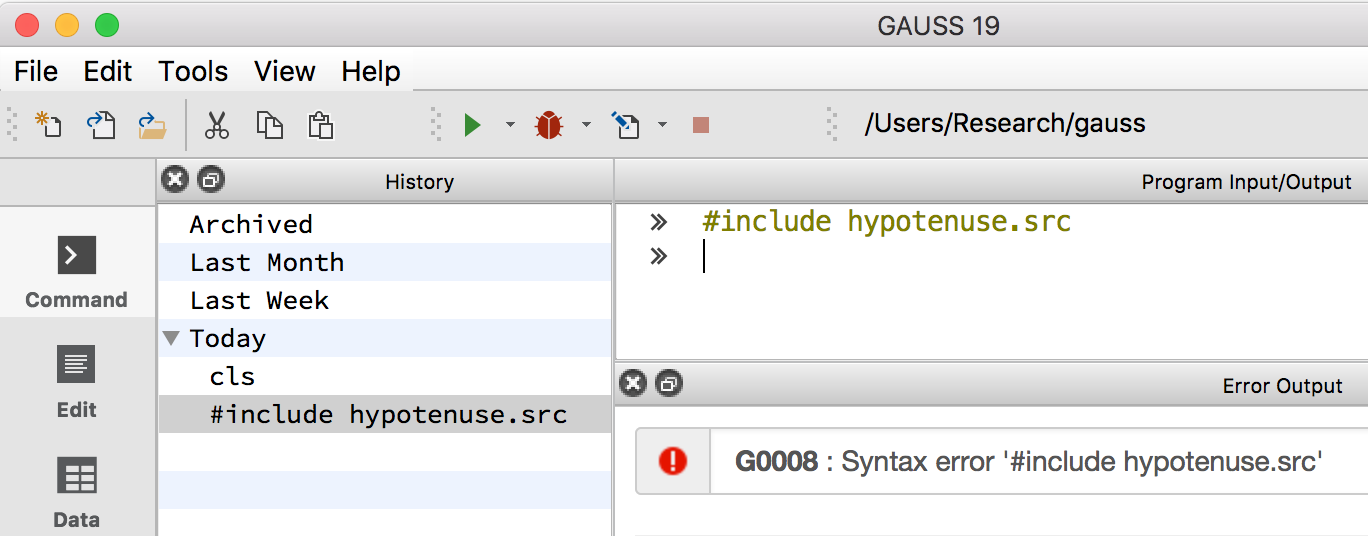 The second most common error with
The second most common error with #include occurs when either:
- Entering the
#includecommand in the Program Input/Output window. - Running a
#includestatement by right-clicking and selecting Run Selected Text, or Run Current Line.
Either of these will return an error like this:
G0008: Syntax error '#include hypotenuse.src'
This is because #include statements must be run as part of a program file.
How can I resolve the problem?
If you would like to execute the command #include <filename> in the GAUSS Program Input/Output window, simply replace #include with run.
// Use the 'run' statement at the GAUSS command line run hypotenuse.src
The run command will execute the code in the file exactly as if the #include statement was run as part of a program file.
Conclusions
Today we have learned:
- What the
#includecommand does in GAUSS. - Why it is used.
- The two most common errors associated with its usage.
- Methods to resolve common errors.
Code and data from this blog can be found here.